Prostatitis is an inflammatory process associated with inflammation of the prostate gland (prostate gland) in men. The disease most often occurs in men over 30 years. The disease causes pain in the lower back, perineum or pelvis, is accompanied by a violation of the normal process of urination, and in severe forms leads to erectile dysfunction and serious problems in relationships with a partner.
About a quarter of infertile couples suffer from the male factor that contributes to the impossibility of conception. Male infertility is a violation of the quality of sperm and their quantitative composition during ejaculation.
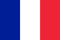
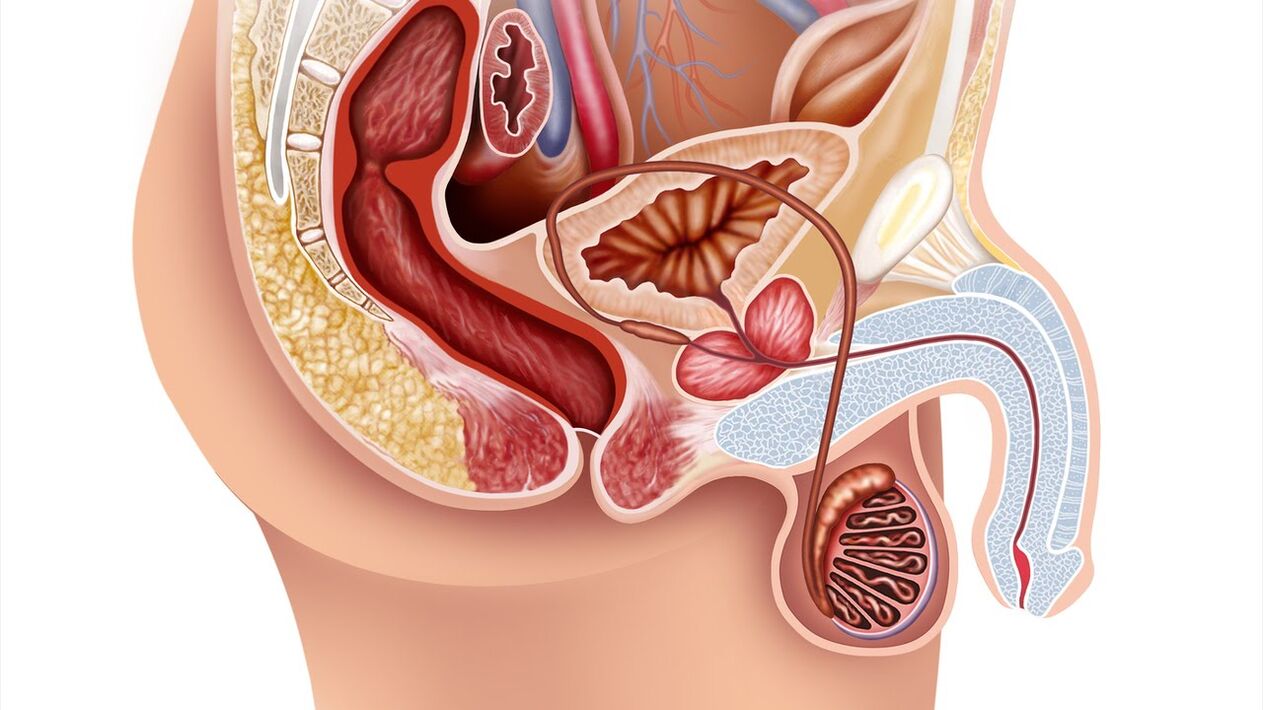
The prostate gland (prostate) belongs to the male reproductive system. It is chestnut-shaped, located in front of the rectum, under the bladder, and covers the urethra. When the prostate gland becomes inflamed, it squeezes the urethra, which further causes problems with urination. The main function of the prostate is to produce a secretion (fluid) that is part of the sperm and dilutes it, which ensures the normal motility of sperm.
In the practice of a urologist, prostatitis is very common. It can occur suddenly or gradually, can be persistent and long-lasting (chronic prostatitis). The chronic form of this disease is more common than the acute form. Chronic prostatitis ranks fifth among the twenty major urological diagnoses.
Because prostatitis is an active center of infection in the body, it requires mandatory treatment, even if its symptoms do not bother you.
Causes of prostatitis
The list of causes of inflammation of the prostate gland is very diverse:
- diseases of the genitourinary system (cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis);
- sexually transmitted infections (trichomoniasis, gonorrhea);
- infections associated with pneumonia, influenza, tonsillitis, furunculosis;
- chronic constipation, forcing a man to constantly strain;
- a sedentary lifestyle and irregular sex life that led to the stagnation of mystery;
- urinary retention - swollen bladder increases prostate pressure;
- frequent hypothermia (or overheating);
- injuries to the pelvic region;
- hormonal disorders that weaken the immune system.
Very often the appearance of prostatitis is caused by pyogenic microbes: E. coli, streptococci and staphylococci, mycoplasmas, Candida fungi, Trichomonas, tuberculosis bacillus. They multiply very quickly and destroy the prostate tissue, which manifests itself in inflammation.
In most cases, prostatitis is caused by an infection that penetrates the prostate gland through the urethra. It enters the body through the blood or lymph, passes through the bladder or rectum.
It is important! Decreased immunity is very dangerous for a patient with chronic prostatitis, because the prostate gland is quickly inflamed by fatigue, stress, lack of sleep, nutrition and other negative factors.
With a sedentary lifestyle and lack of regular sex life, the blood supply to the pelvic organs deteriorates, leading to oxygen starvation and blockage of the prostate tissue. A stagnant secret is an ideal environment for the growth of pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation.
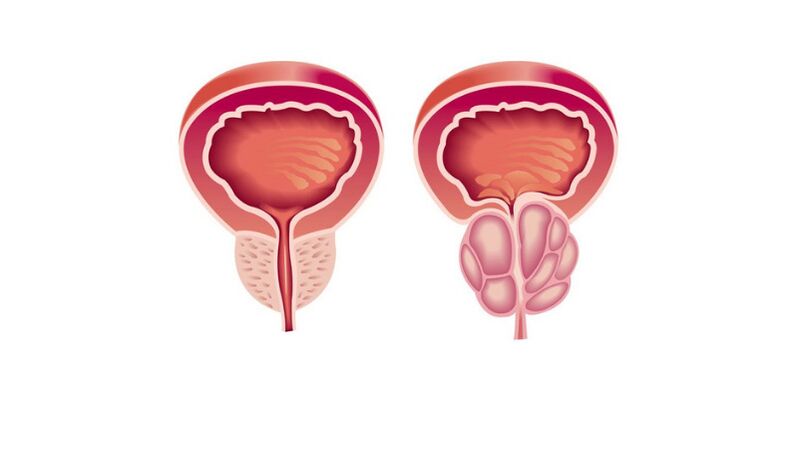
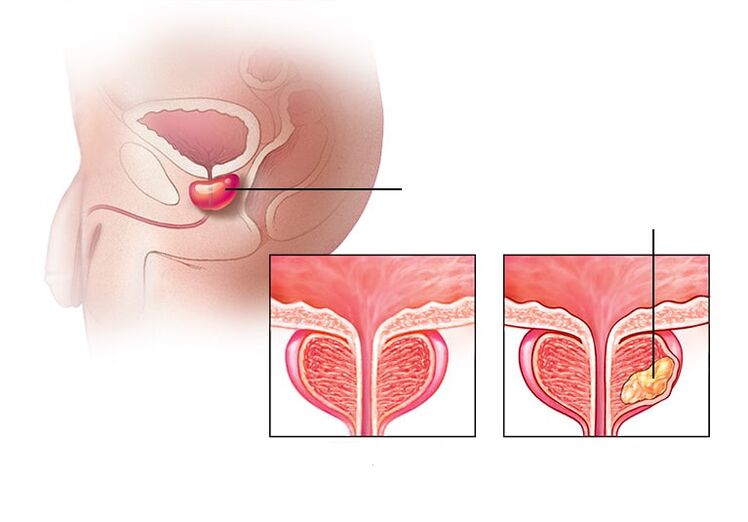
Types and forms of prostatitis
Prostatitis is divided into types and forms depending on the cause of the disease:
They differ by type:
Bacterial prostatitis- Inflammation caused by infection. Bacterial prostatitis occurs in both young and old men.
congestive prostatitis- Inflammation caused by stagnation of secretion. It develops in men who lead a sedentary lifestyle and do not have a regular sex life. This form can quickly be completed with an infection, and then the stagnant process is complicated by the bacterial form.
Calculus prostatitis- Stones are formed in the prostate gland. Untreated chronic prostatitis can cause this complication. The disease affects older men who do not follow the advice of a urologist.
They differ in the form of flow:
Acute form of prostatitis- It is an inflammation of the prostate gland caused by an infectious agent characterized by the appearance of edema and purulent foci in the tissues. 30-58% of men of reproductive age (30-50 years) have such a diagnosis.
Chronic form of prostatitisis characterized by persistent or recurrent urogenital symptoms caused by a bacterial infection in the prostate gland. The chronic form accounts for 10% of all cases of prostatitis.
Symptoms of prostatitis
Generalsymptoms of inflammation of the prostate glandthese are:
- pain in the lower back;
- feeling of discomfort during bowel movements;
- pain in the perineum or pelvic region;
- disorders of the lower urinary tract.
The acute stage of prostatitis is accompanied by a general intoxication syndrome. The disease is characterized by an acute manifestation of symptoms with a bright clinical picture:
- sudden increase in body temperature, chills, nausea, vomiting and malaise;
- pain syndrome and tremors in the joints and muscles;
- increase in prostate size and perineal discomfort;
- frequent urination and urinary retention.
Against the background of individual inflammatory processes may develop a purulent-septic disease that affects the blood. In this case, the patient should be hospitalized immediately: treatment of prostatitis with sepsis should be carried out only in the clinic.
Atchronic prostatitis of bacterial natureSymptoms are usually absent, so treatment begins only when an infection of the urinary system is detected, which manifests itself in the background of aggravation of the disease. In this situation you can observe:
- pain during ejaculation;
- appearance of blood in the discharge;
- presence of discharge from the urethra;
- erectile dysfunction may develop.
If the examination does not show that the chronic pain is caused by pathologies of the prostate gland, then we deal with it.chronic non-bacterial prostatitisor so-calledchronic pelvic pain syndrome. The quality of life of a person with this disease is significantly reduced, because it leads to various psychological and sexual disorders:
- increased fatigue;
- feeling of helplessness;
- erectile dysfunction;
- painful ejaculation;
- pain after sexual intercourse, etc.
Similar symptoms can be attributed to other urological diseases, so prostatitis cannot be diagnosed by symptoms alone. For example, urinary incontinence and pain in prostate adenoma, cystitis, various oncological tumors of the genitourinary system, etc.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the prostate gland
After identifying the first signs of inflammation of the prostate, the patient should immediately contact a doctor - a urologist. The doctor should rule out many diseases with similar manifestations and determine what type of disease they belong to.
To confirm that the patient has no other diseases (eg, appendicitis, oncology, inflammatory processes in the bladder and kidneys, prostate adenoma), the doctor should conduct the necessary examinations:
- collection of anamnesis (questioning of the patient);
- general inspection;
- rectal examination;
- study of the secretion of the prostate gland;
- analysis of sexually transmitted infections;
- Ultrasound examination of the prostate gland, scrotum and pelvic organs.
At the time of admission, the urologist should clarify with the patient the duration of clinical manifestations of the disease, the location and nature of pain (eg, perineum, scrotum, penis and inner thigh), characteristic changes (presence) in sperm. pus and blood).
The doctor diagnoses chronic bacterial prostatitis with symptoms lasting at least three months.
The survey includes:
- Digital rectal examination of the gland to determine the degree of growth of the prostate and its consistency.
- Analysis of prostate secretion, urine and / or ejaculation.
- Detection of urogenital infection.
- Urodynamic research.
- Ultrasound examination of the urinary system (kidneys, prostate, bladder with determination of residual urine).
- Cultural examination of prostate secretion and microscopy of various parts of urine and prostate secretion.
- Androflor is a comprehensive study of the microbiocenosis of the urogenital tract in men with PCR, which will determine the qualitative and quantitative composition of the microflora.
After determining the cause of the disease, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment. Keep in mind that standard methods can detect infection in only 5-10% of cases, resulting in prostatitis.
The patient must undergo a thorough diagnosis, because the success of treatment will depend on the accuracy of the results.
Treatment of prostatitis
When a urologist diagnoses, determines the cause and form of prostatitis, he must prescribe treatment.
The leading role in the treatment of this disease is given to drug therapy:
Antibacterial therapy
In the first stage of therapeutic therapy, it is necessary to eliminate the inflammation. Antibiotics are the main treatment for acute bacterial prostatitis and are recommended for chronic bacterial prostatitis. The doctor chooses an antibacterial drug depending on which bacterium is causing the disease. The patient will have to take oral antibiotics for 4-6 weeks. The resolution of chronic or recurrent prostatitis takes longer. Hospitalization may be required for very severe manifestations in which an intravenous course of antibiotics will be given. This usually happens with acute bacterial prostatitis.
Treatment with alpha1-blockers
A doctor who has difficulty urinating prescribes alpha1-blockers, which facilitate urination and relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder. Muscle relaxants will relieve pain caused by swelling of the prostate gland, which puts pressure on adjacent muscles. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will help relieve the painful syndrome.
The doctor may also prescribe ancillary drugs: biostimulants, extracts of various plants and insects in the form of rectal suppositories. Unfortunately, the use of drugs alone in the treatment of prostatitis remains insufficient.
In the treatment of this disease, the principles of sequence of actions must be followed. The treatment of prostatitis is always complicated.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of prostatitis
In addition to the categories of chronic prostatitis, you can use physiotherapy methods:
- prostate massage (prostate);
- laser therapy;
- microwave hyperthermia and thermotherapy;
- electrical stimulation with currents modulated by skin or rectal electrodes;
- acupuncture (acupuncture).
Alternative methods such as hirudotherapy (treatment with medical leeches) are sometimes used to treat prostatitis, but the effectiveness and safety of this method has not been proven.
Presentation of stem cells
Cell therapy (stem cell injections) is a promising method for the treatment of prostatitis today, at an early stage of development. There can only be hypotheses about the mechanisms of stem cell implantation in the prostate and the empirical data obtained by different groups of researchers.
Surgical treatment of prostatitis
Surgical methods are used to treat complications of prostatitis (abscess and pus of seminal vesicles).
Treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome requires separate consideration. Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis does not require treatment.
Diet and lifestyle for prostatitis
Prostatitis does not require a special diet, but eating plenty of vegetables, lean meats and dairy products will help improve bowel function. It is necessary to enrich your body with enough fiber, foods rich in vitamin E (wheat germ, corn oil, etc. ), to replace sugar with natural honey. With inflammation of the prostate gland, proper nutrition will help improve bowel function and reduce the likelihood of recurrence or speed up recovery. The patient should limit his coffee intake, abstain from alcohol, drink plenty of fluids and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Prophylactic measures to prevent prostatitis
When a man leads a healthy lifestyle: eats properly, does sports, then the chances of developing chronic prostatitis are very low. Abstinence from bad habits and casual sex is the prevention of this disease.
It is important! There are primary and secondary prophylaxis to prevent the development of prostatitis in men.
Initial- aimed at preventing the occurrence of the disease. These include a balanced diet, physical activity, timely treatment of any infectious diseases of the body, and regular protected sexual intercourse, etc.
Secondary- aims to prevent the recurrence of existing chronic prostatitis and provides regular examination by a urologist and prophylactic treatment with multivitamins, restorative drugs and sports.